Biocompatibility is critical in the medical device industry, and it refers to how well a material used in a device interacts with our living tissues without causing any negative effects. It’s all about keeping us safe and minimizing any potential harm. When a medical device is implanted or comes in contact with our bodies, it’s important that it functions properly without triggering any unwanted reactions, inflammation, or damage to our tissues. Think of it as a compatibility test between the device and our bodies, ensuring they get along harmoniously. So, biocompatibility plays a vital role in ensuring the device is not only effective but also doesn’t cause any harm along the way.
A Critical Aspect of Medical Device Materials
The primary goal of any medical device is to improve health and well-being. When thinking about medical cable assemblies, they’re responsible for connecting different components together, such as transmitting signals or delivering power. It’s important that these cables are providing to the health and well-being of patients, but that they’re also safe for patient use.
For instance, manufacturers and engineers perform tests and assessments to ensure that the materials used in cables don’t cause any harm or adverse reactions. They examine if the materials can provoke our immune system or cause irritation. They also check if there’s any risk of the materials releasing harmful substances that could affect our health. All of this is done to make sure that materials are compatible with bodies, minimizing any potential risks and ensuring the overall safety and effectiveness of the medical device.
Biocompatibility and ISO 10993
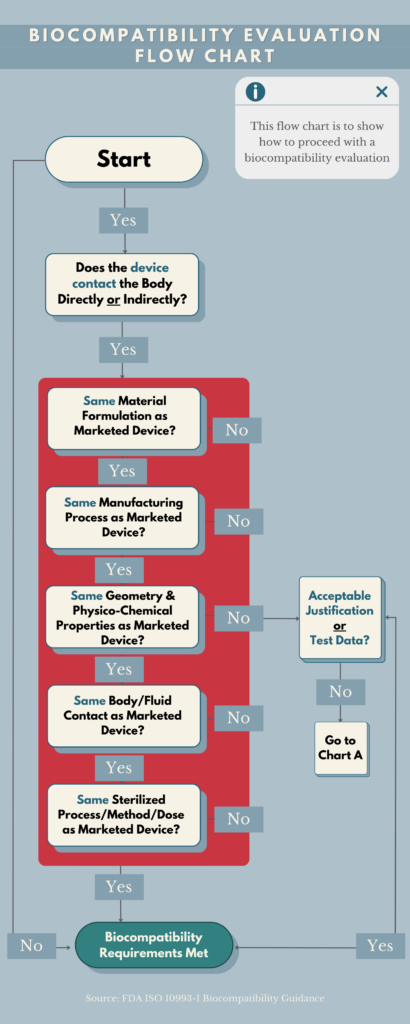
There are specific regulations and standards that guide the development and evaluation of cable assembly materials. These standards outline the requirements and tests that materials must undergo to ensure their biocompatibility.
For instance, there are standards such as ISO 10993, which provides guidelines for assessing the biological safety of medical devices. This includes conducting tests to determine the potential risks associated with materials used in cable assemblies.
These tests may evaluate factors such as:
- Cytotoxicity (cell compatibility)
- Sensitization
- Irritation
- Systemic Toxicity
By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can ensure that cable assembly materials meet the necessary biocompatibility requirements.
See figure 1 on the right as an example for a compatibility evaluation flow chart break down per ISO 10993:
For more information on other FDA and ISO requirements, read more in this blog.
Biocompatible Materials
Biocompatible materials are those that have been specifically designed and tested to be compatible with living tissues. These materials undergo rigorous evaluations to ensure they meet the necessary biocompatibility standards.
Examples of Biocompatible Materials
Some examples of biocompatible materials used in cable assemblies include:
- Medical-Grade Silicone
- Stainless Steel
- Titanium
- Thermoplastic Polymers and Elastomers
These materials have been extensively tested and proven to be safe for use in medical devices, providing excellent biocompatibility properties.
Wrapping Things Up
Biocompatible cable assembly materials play a critical role in the performance and safety of medical devices. These materials exhibit essential characteristics such as non-toxicity, non-allergenicity, and resistance to degradation. By utilizing biocompatible materials, medical devices can function optimally, delivering accurate results, improving patient comfort, and reducing the risk of complications. The ongoing advancement in biocompatible materials continues to drive innovation in the medical device industry, ensuring the highest standards of safety, effectiveness, and patient well-being.
Contact Us for more information. We’re here to help. Let’s get started on your next medical cable assembly project, today!
Here are some more ClearPath Medical blogs that might interest you.
Love what you see? Sign up for our newsletter to get the latest updates on our company, worldwide and more.

